When using the inheritance the problem arises of determining the right type to use for Association. In other words, if a master type is the type associated with inheritance, it is unclear what specific type of an inheritance hierarchy is a master.
For example, there is the following model:
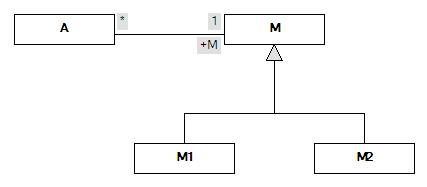
Class А has a masters М, which has at least two of the heir M1 and M2.
Accordingly, if a data object a (an instance of class A) that his master could be an instance of any of classes M, M1, M2.
Service data stored object a with the master m1.
The problem is: if now, the data service reads an object а as he learns» «that the master belongs to the class M1 and, accordingly, is in the same data structure? After all, he is only known type M, but fundamentally impossible to know what types inherited from M.
the Attributes of a typeusage and PropertyTypeUsage
To resolve the problem, you can use special metadata that allows you to specify that a property M (link to the artisan class) in the class data A, in this particular (practical) case, can take only values of type M, but also M1, and M2. In this example, the types M1 and M2 are called types used.
Used types are specified:
1.Attribute a typeusage for workman/metalowego properties of the data class, or for class array metalowych objects (derived from DetailArray).
public class A:DataObject
{
private M fM;
[TypeUsage(new Type[]{typeof(M1), typeof(M2)})]
public virtual M M {get{return fM;}set{fM=value;}}
}
public class M:DataObject
{
}
public class M1:M
{
}
public class M2:M
{
}
2.PstrfPropertyTypeUsage attribute for the data class, whose property should be used to specify types. The attribute is similar, however the class is to write clearer than to a specific property, especially when a lot of them. In addition, this entry is used when you want to change TypeUsage` in an inherited class, without overloading properties.
An example entry PropertyTypeUsage equivalent TypeUsage:
[PropertyTypeUsage("M",new Type[]{typeof(M1), typeof(M2)})]
public class A:DataObject
{
private M fM;
public virtual M M {get{return fM;}set{fM=value;}}
}
The Information.CheckUsingType allows you to check inside the property, method, where invoked is compatible with the declared type according to the used types.
TypeUsageProvider.A typeusage
Specifying additional attributes cannot completely solve the problem of used types, as the situation may arise:
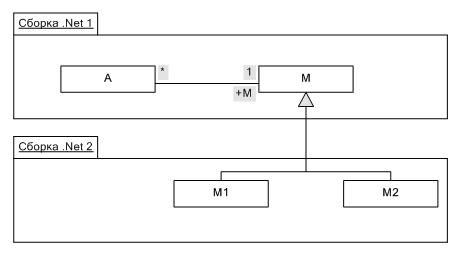
Here, the class ancestor is in a separate Assembly, so TypeUsage to register will fail, as in the first Assembly it is necessary to know the types M1 and M2 (located in the second Assembly, reference the first), and reciprocal link assemblies to each other according to .Net impossible. The case could be complicated by the fact that the developer that creates the Assembly 2, in principle, has no access to the source code of the Assembly 1 (and, therefore, it cannot merge assemblies into one). Of course, TypeUsage prescribe and in this case, however, you are using a static property of a static class TypeUsageProvider.TypeUsage. It contains a variety of functionality for managing used types: you can specify the used types, learn/change their composition, etc.
At workman communications used types you can specify for the masters of any nesting. It is necessary to specify the names of user controllable properties through the point. Method TypeUsageProvider.A typeusage.GetCombinedTypeUsage you can get all types in a single collection.