Common approaches to systems integration
Systems integration in most cases is a forced measure, aimed at improving the efficiency of business processes that use the information system [http://citcity.ru/16663/].
Consider the basic approaches to integration of information systems, demonstrating the potential solutions to the various problems of the companies associated with the necessity of interoperability.
1. No integration between systems
The company uses three separate information systems: «Inventory system» (accounting and analysis of movement in the warehouse), «CRM system» (accounting and analysis of sales and other customer relations) «and» Accounting system (accounting and financial analysis). Between them there is no information exchange.
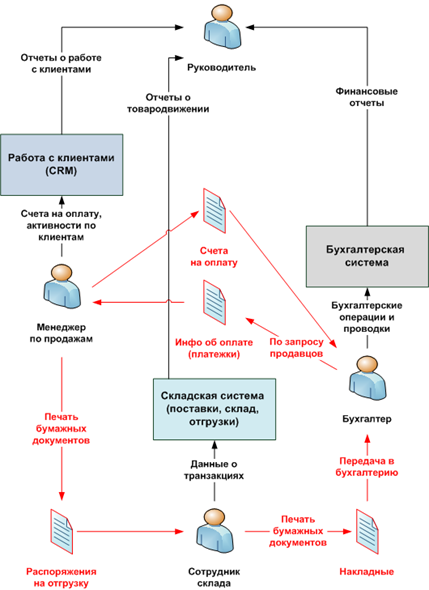
This leads to the fact that the sales after billing your clients have to print them up and carry to the accounting Department. In accounting, they are recorded in the accounting system. Accounting records the flow of money into the account. Sales managers, not having the ability to get payment automatically in the CRM system, are forced daily to inquire in accounting of receipt of money from customers. In such a situation, there is a large flow of documents between managers, accounting and the warehouse, and also double check the action (once in the inventory system, for the second time in accounting).
If you count the cost of company-paid time for employees to perform duplicate procedures in different systems (highlighted in red in the diagram), you can get a significant share of the total costs of the firm.
2. Vertical integration
In line with this approach, the systems are integrated on the principle of functional expertise. For example, in this case, the selected two of expertise: operational accounting and accounting. While accounting is vertically above the operative account. In our example, subsystem operational accounting deliver data to the subsystem of accounting.

This significantly reduces the manpower needed to duplicate and paper operations, however, there are two aggravating moment.
First, such a system is extremely difficult to expand functionally. For example, a company may want to create a subsystem-expertise» «Analyst, which will be vertically located above the examination «Accounting». This examination is largely based on data «Operational account of the». Therefore, in addition to the development of the subsystem» «Analyst will have to modify the subsystem «Accounting» in order to get her and kept her from «Operational accounting» additional information.
Second, there remains significant potential for integration within the same functional expertise.
3. Integration «qmc many-to-many (star, spaghetti)
Under this approach, each of the companies used in subsystems may, if necessary, to appeal to the functionality of any other subsystem, while each subsystem may also be used by any other subsystem. This type of relationship between the elements is called «many-to-many».
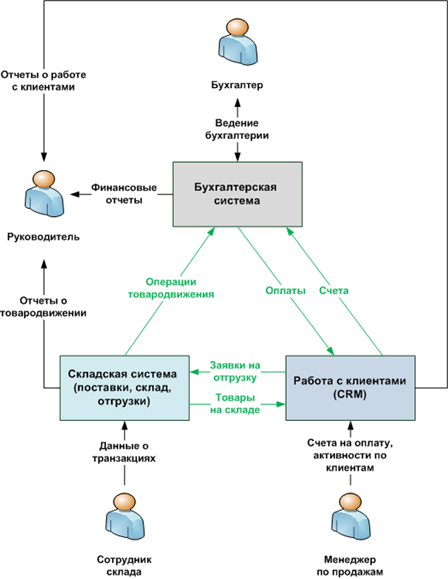
In this case take place with almost unlimited possibilities of integration of the subsystems to each other (of course, if technologically subsystem allow you to do this).
But, on the other hand, the costs to support such integration schemes is growing exponentially with increasing number of integrated subsystems. For example, if in our case, we need to change something in the accounting subsystem (for example, to change its object model), it can lead to the necessity of processing all other subsystems use it, because calls to the old object model will fail. For three interacting systems, this can be not so critical, but for thirty very.
4. Horizontal integration
This approach involves the use of specialized» «intermediate (middleware) - the so-called enterprise service bus. The main objective of this is to store the repository functionality of enterprise applications connected to it, and making use of these functions by other applications, also connected to this bus. Communication between applications can for example be in the form of messaging or calling functions published as Web services. System connection to the bus is done by creating a special adapter for each system. Then «published» functions of the system become available to other connected systems.
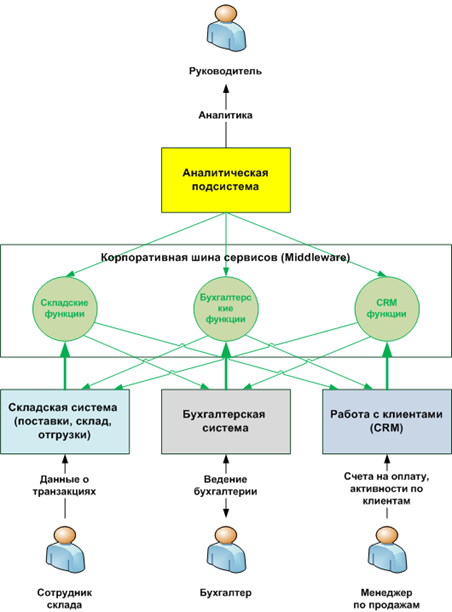
For example, a CRM system when connected to the bus publishes its functions for working with a client database. The bus provides the possibility of their use accounting and warehouse systems. In turn, the CRM system gets an opportunity with the accounting and inventory data.
The advantage of this approach is that the systems can be replaced within the existing specifications published functions. However, no changes in other systems is not required. Moreover, the connection of the new system sufficiently standardized and simplified. For example, it is possible to connect a new system» «Analyst, who will immediately receive access to all other systems.
5. No need for integration
By far, the best integration is the lack of need for it. For example, all of the above subsystems can be implemented as functional modules of the ERP system of any vendor. In this case, the need to integrate eliminated, as the system is initially uniform, ensuring much greater coherence between the functional modules than any of the above integration between the different systems.
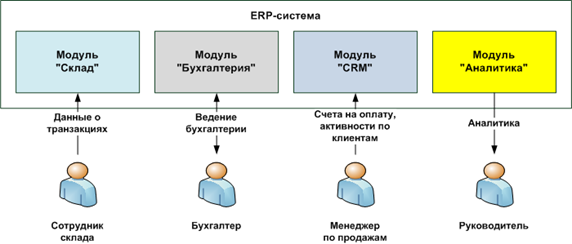
Objects and methods of integration of systems
Earlier in the description of approaches to integrating systems, we examined each information system as the» «indivisible object. However, the information system is a combination of several components, therefore, speaking about the integration of information systems, it is more correct to talk about integration components.
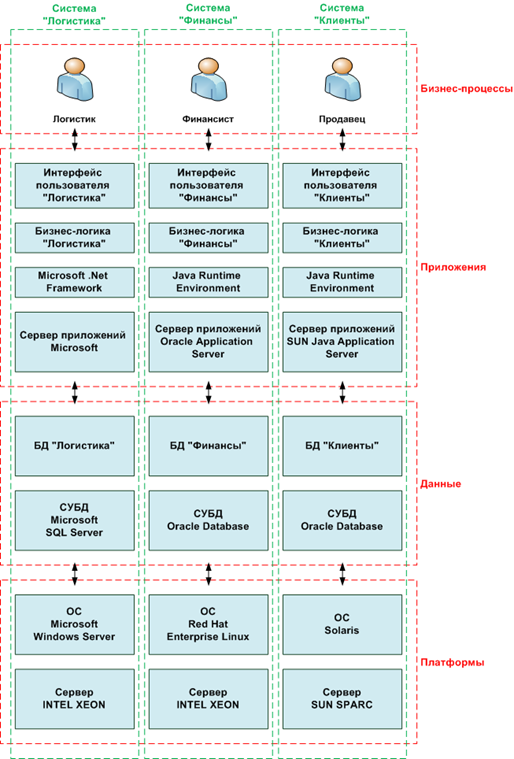
Usually, the information system contains the following components:
- The platform on which operate the remaining system components, including equipment (hardware) and system software.
- The data on which the system works. Consist of DBMS and databases.
- Applications that implement the business logic for working with the data system. Consist of business logic, user interface, ancillary components (frameworks), and application server, which provides storage and access to application components.
- Business processes, which represent the scenarios of users with the system.
Therefore, the integration of information systems is to integrate one or more components of information systems to be integrated (integration objects):
- Integration platforms
- Data integration
- Application integration
- Integration of business processes
1. Integration platforms
The objectives of the integration platforms are:
- Ensuring interoperability between applications running on different hardware and software platforms (e.g., between applications running on Windows servers, Solaris, Linux, etc.).
- To ensure that applications developed for one hardware platform, other software and hardware platforms (e.g., Windows-based applications on platforms Linux, Solaris, etc.).
There are several approaches aimed at achieving these goals. Within each approach there are various technologies [http://citcity.ru/10881/]:
- Remote procedure call (RPC, Web-services, REST, etc.)
- Middleware (Microsoft.Net, Java Runtime)
- Virtualization
Technology remote procedure call (in a broad sense, a procedure is defined as some functionality of the application) allow you to publish the procedure and allow the call (transfer input parameters and produce output results) for applications running on other platforms.
The concept of the software of the intermediate layer (framework, runtime, virtual machine) is to develop software applications are not using the services of a specific operating system (e.g. Windows API), and using the services of middleware. Developers of middleware created for its implementation under different operating systems, which transmit calls to the corresponding functions in frawork calls the appropriate operating system. A typical example is a Java technology Runtime Environment. Applications developed for this technology works on all hardware and software platforms (Windows, Linux etc.) without any modifications of the applications themselves. Similar opportunities are provided by Microsoft .Net Framework.
Interesting and innovative concept is virtualization» qmo. The integration of platforms, it is relevant in so far as it allows to substantially simplify the use of different platforms and, therefore, the use of systems that require for their functioning the presence of specific platforms. If no virtualization possible simultaneous operation N operating environments on N servers, the use of virtualization technologies allows to ensure the functioning of operating environments N to M servers. If N > M this allows to reduce hardware costs through more efficient use. If N < M is a simple way to increase performance of their systems. For example, virtualization enables you to deploy and simultaneously use on a single physical server multiple operating systems: Windows, Linux, etc. On each of these» «virtual servers can be deployed appropriate systems that will be available at the same time. Examples of virtualization technologies: Microsoft Hyper-V, KVM, OpenVZ, Virtuozzo, VMware, Xen, etc.
2. Data integration
By definition, an information system works with data. The vast majority of cases, the system incorporates a database to store them. Integration at the data level involves data sharing among different systems. Data integration can be easier than application integration, as industrial databases, which usually store data information systems, have developed the ability to programmatically access data from other applications. The apps themselves can thus have very limited possibilities of the software (outside of their own user interface) use its functionality to external systems.
Approaches to data integration:
- Universal data access
- Data warehouse
Technology universal data access allow to provide uniform data access to various DBMS. A mediator to work with a specific DBMS in this case is the driver for your DBMS. For example, the same SQL query to retrieve data SELECT * FROM TTABLE can be used to retrieve data from the table TTABLE stored in different DBMS. This allows to abstract from the specifics of a particular DBMS and easily integrate data stored in different DBMS. The most common technology in this class: ODBC, JDBC, ADO.NET. In addition, today’s widespread technology object-relational mapping (ORM) that also allow to abstract from details of interaction with konkretnymi DBMS. Examples of such technologies are Entity Framework, Hibernate, NHibernate, Flexberry ORM.
The concept of data warehousing is to create a corporate data warehouse. Data warehouse – a database that stores data collected from the databases of various information systems, for the purpose of their further analysis. For example, there may be a single repository of company data, which collected information from accounting, operational systems, external systems of our partners. For data warehousing technology is used (OLAP) is different from the technologies of creation of operational database (OLTP). This is mostly done to improve performance of complex analytical queries in many aspects (multidimensional queries). Approaches to the creation and filling of data warehouses is reflected in the paradigm of ETL (extraction, transformation, loading = extraction, transformation and loading). Technologies and tools for analysis of large data sets to identify patterns of the subject area combined the concept of Data Mining» qmo. The term for a set of technology data warehouse and tools to ensure the translation of transactional business information in chelovecescie a form suitable for business analysis – Business Intelligence» qmo.
3. Application integration
Integration at the application level implies the use of ready functions of applications by other applications. For example, by developing electronic document management system, it is possible to use this system as a text editor MS Word instead of having to develop your own text editor. Or, for example, VIA the Call center, receiving an incoming call from the client that has the ability to access the billing system for the balance test (input the phone number of the caller, the output of the current balance) and depending on the state of the balance connected to an operator or to automatically inform about the need to Fund your account. The structure of the database of the billing system is its internal information are published for a specific function, allowing other systems to work with specific data.
It is worth mentioning the following approaches to application integration:
- Application programming interfaces
- Messaging (Enterprise service bus)
- Service-oriented architecture
- Integration of user interfaces
The software interface of a particular system represents the published» «functionality of the system, which can be used from the outside. The functionality may be published in the form of a set of functions (example – Windows API) or object model (objects with properties and methods, example – object model of Microsoft Office applications).
In most cases, the integration of multiple systems is to transfer information between them, for example, in the form of request-response. If systems operate in heterogeneous distributed environments, it is of fundamental importance to provide warranty, safety, and handling information delivery between applications. These and other principles are realized in corporate messaging systems. In this case we are talking about exchanging messages between applications, not people, as, for example, in the case of E-mail or instant messengers. The functionality of these systems sufficiently transparent – receipt of a message from one application, transportation, rule-based and transfer this message to another application. This may be the message encryption (for the inability to read data in transit), digital signature (for protection against intentional changes to the data during the path message), configuring subscriptions (to send a single message to multiple applications), the metadata definition for messages (to facilitate the use of messages with complex content structure) and others [https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Сервисная_шина_предприятия].
Service-oriented architecture (SOA) is a logical continuation of the concept of Web services, which consists in the publication of functional blocks any app that allows you to access another application through the Web. Web (HTTP) in this case is attractive due to the possibility of its use and, therefore, the use of published Web applications functionality on any hardware and software platforms. Web services – small software add-on functionality of the application that converts a call received via the Web, the internal application function calls and returns the results back. The basic ideas of SOA are [https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Сервис-ориентированная_архитектура a]:
- Publish functionality of enterprise applications in the form of Web services. Organize published services in the catalog.
- Construction based on Web services new applications by a combination of both.
The cost of creating new applications based on existing Web services will be significantly lower than developing applications from scratch «qmc or extensive integration with other systems.
For example, the company (operator) there is a Service Desk (customer technical support) and billing system (billing system). The company faces the task of making a new system «Personal subscriber Cabinet», in which the subscriber could, via the Internet to view your account status and report the fault. For this the company is to create a «Personal account» with its own database that is synchronized with the database of the billing system and Service Desk that uses Web services «Card subscriber» (published functionality of the billing system) and «to Create a request to tech support» (published functionality of the Service Desk system). It is obvious that all the work on the new «Personal account» is creating a Web user interface on the website of the company.
Also common approach is the integration of user interfaces. For example, to create applications «single window». The simplest example of frames on a Web page. Inside each frame contains a separate Web application. Thanks to the frames, all these apps appear on the screen at the same time. User interfaces Web applications are easy to integrate, however, there are opportunities to integrate and classical» «user interfaces and their fragments (ActiveX).
4. Integration of business processes
The most holistic approach to systems integration is integration at the level of business processes. As part of the integration business processes and applications integration, and data integration and, equally importantly, of the people involved in this business process. Integration at the level of business processes is the most natural» «for organizations, since their activities consist primarily of business processes, not applications, databases and platforms.
The idea underlying the integration of business processes, is quite simple:
- To make the scenario of a business process in the organization, describe it, operations of user interaction with various systems in between. Thus, a business process is an element that is logically integrating various systems. The script is created using specialized software, which will continue to manage this business process scenario.
- Interaction with systems within the business process details are described in terms of information exchange: interchange formats used by the services, applications, events, rules, policies, etc.
- Integrating software with the help of which describes the scenario of a business process, are connected through adapters integrable systems involved in the business process. Thus, it becomes possible automated exchange of information between systems.
- Ready-to-execute business process is displayed on «remote control» Manager, with which he can start and stop business processes, track their status, enter data and make decisions on individual business processes that require human intervention. and Interactions between systems that do not require human intervention is carried out automatically integrating.